Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, yet many don’t realize how widespread it truly is. Whether you’re noticing more strands in your brush or a receding hairline, understanding the facts can help you take control of your hair health.
This article provides a detailed look at hair loss statistics, covering:
- How many people experience hair thinning globally
- The differences between male and female hair loss
- The most common causes and risk factors
- How age, genetics, and lifestyle play a role
- The emotional impact of losing hair
- The latest trends in prevention and treatment
Let’s explore the numbers and what they mean for you.
1. How Many People Lose Hair Worldwide?
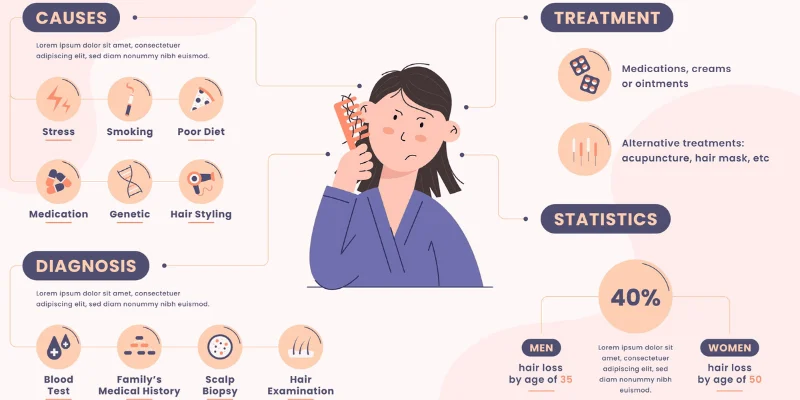
Hair loss is far more common than most people think. Research shows:
- 50% of men will experience noticeable hair loss by age 50.
- Approximately 40% of women will experience visible thinning by the age of 40.
- 80 million Americans (both men and women) have hereditary hair loss.
Hair Loss by Region
- Asia has high rates, particularly in China and Japan, where stress and pollution are significant contributors.
- Europe and North America follow closely, with genetics being the most significant factor.
- Alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition characterized by patchy hair loss, affects approximately 2% of people worldwide.
These numbers prove that hair loss is a widespread issue, not something that only happens to a few unlucky people.
2. Hair Loss in Men: When and Why It Happens
Male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) is the most common type of hair loss in men. Here’s how it progresses:
By Age
- 25% of men start losing hair before age 21.
- 66% of men have thinning hair by age 35.
- 85% of men have significant hair loss by age 50.
Why Do Men Go Bald?
- Genetics – If your father or grandfather was bald, your risk is higher.
- Hormones – DHT (a form of testosterone) shrinks hair follicles over time.
- Stress & Illness – Physical or emotional stress can speed up hair loss.
- Poor Nutrition – Lack of protein, iron, or vitamins weakens hair.
The Norwood Scale: Stages of Male Baldness
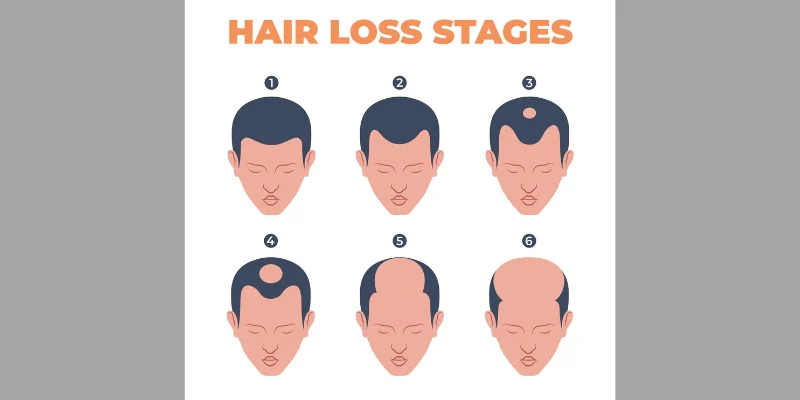

Doctors use this scale to measure male hair loss:
- Stage 1 – Minimal or no recession.
- Stage 2 – Slight recession at temples.
- Stage 3 – Deepening recession (M-shaped hairline).
- Stage 4-6 – Thinning crown, leading to full baldness.
The earlier you notice hair loss, the better your chances of slowing it down.
3. Hair Loss in Women: Causes and Patterns

Women experience hair loss differently than men. Instead of a receding hairline, they usually see overall thinning.
By Age
- 20% of women in their 20s and 30s notice thinning.
- 40% of women see visible hair loss by menopause.
- 50% of women over 65 have significant thinning.
Common Causes in Women
- Hormonal Changes – Pregnancy, birth control, and menopause affect hair growth.
- Medical Conditions – Thyroid disorders, anemia, and PCOS contribute.
- Traction Alopecia – Tight hairstyles (ponytails, braids) pull out hair over time.
- Stress & Diet – Crash diets or extreme stress lead to shedding.
The Ludwig Scale: Female Hair Thinning Stages
Doctors classify female hair loss in three stages:
- Type I – Mild thinning that’s barely noticeable.
- Type II – Wider part and reduced volume.
- Type III – Visible scalp through thinning hair.
Unlike men, women rarely go completely bald, but thinning can still be distressing.
4. What Really Causes Hair Loss?
Hair loss happens for many reasons. The most common include:
1. Genetics (Androgenetic Alopecia)
- Responsible for 95% of male baldness and 70% of female thinning.
- Runs in families—if your parents had hair loss, you likely will too.
2. Medical Conditions
- Thyroid disorders (both overactive and underactive).
- Anaemia (low iron levels).
- Autoimmune diseases (like alopecia areata).
3. Stress & Shock (Telogen Effluvium)
- Significant stress (surgery, illness, childbirth) pushes hair into a resting phase.
- Hair falls out 3-6 months later, often in clumps.
4. Poor Nutrition
- Lack of protein, iron, zinc, or vitamin D weakens hair.
- Extreme dieting or eating disorders trigger hair loss.
5. Hair Damage
- Overuse of heat tools, bleach, or tight hairstyles.
- Chemical treatments that weaken hair follicles.
Knowing the cause helps you choose the right treatment.
5. The Emotional Side of Hair Loss
Hair loss isn’t just physical—it affects mental health too:
- 63% of women say thinning hair lowers their self-esteem.
- Men with balding often feel older or less attractive.
- Many people avoid social events due to embarrassment.
How People Cope
- Some wear hats or wigs to hide thinning.
- Others try hair fibers or scalp concealers.
- Support groups help people feel less alone.
If hair loss is affecting your confidence, talking to a doctor or therapist can help.
6. Are More People Losing Hair Now?
Yes, experts have noted a rise in hair loss rates, particularly among younger adults.
Why Is This Happening?
- Increased stress (work, finances, social pressure).
- Poor diets (fast food, low-nutrient meals).
- Environmental factors (pollution, hard water).
- More awareness (people seeking help earlier).
Future Trends
- Hair transplants are growing in popularity.
- Laser therapy and PRP treatments are becoming more accessible.
- Better medications are being developed.
The sooner you address hair loss, the better your results.
7. What Can You Do About Hair Loss?
Medical Treatments
✔ Minoxidil (Rogaine) – A topical treatment that slows hair loss.
✔ Finasteride (Propecia) – A pill that blocks DHT (for men only).
✔ Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) – Stimulates hair growth.
✔ PRP Therapy – Uses your blood to boost hair growth.
Lifestyle Changes
✔ Eat a balanced diet (protein, iron, vitamins).
✔ Reduce stress (exercise, meditation, therapy).
✔ Avoid harsh hair treatments (bleach, tight styles).
Surgical Options
✔ Hair transplants – Move hair from thick areas to thin spots.
When to See a Doctor
- If you’re losing more than 100 hairs a day.
- If you notice sudden bald patches.
- If hair loss is affecting your mental health.
8. Final Thoughts: Don’t Ignore Hair Loss
Hair loss is common, but that doesn’t mean you have to accept it.
- Check your family history – Genetics play a significant role.
- Watch for early signs – Thinning temples, widening part, or excessive shedding.
- Act fast – The sooner you treat it, the better your results.
Whether you try medications, lifestyle changes, or professional treatments, there are ways to slow, stop, or even reverse hair loss.
Key Takeaways
✅ 50% of men and 40% of women experience hair loss.
✅ Genetics, hormones, and stress are major causes.
✅ Early treatment works best—don’t wait.
If you’re worried about hair loss, talk to a dermatologist today.





